>>Stream : A stream is defined as a flow channel into which surface runoff discharge from a specific basin drains and flows along a natural slope.
>> Catchment: The area of a land draining into a stream or a water course at a given location is called as catchment.
#Classification of stram:
1. Ephemeral Stream: a stream which carry water only in rainy season and remain dry during the remaining period is called ephemeral stream.
2. Perennial Stream : A stream that carry discharge throughout the year is classified as perennial stream. Example Ganga and Brahmaputra river.
3. Influent Stream : When water will flow from river bed to the groundwater table then that stream is classified as influent stream.
4. Effluent Stream : When water will flow from groundwater table to the river bed then that stream is called as effluent stream.
Note: A stream can neither be influent nor be effluent throughout its length.
5. Intermittent Stream : A stream that acts as an influent stream for some period and effluent stream for other period is classified as intermittent stream. Example : Tributaries of River Kosi.
#Procedure to find stream discharge :
1. Measurement of Stage:
Stage of a river is water surface elevation measured above the datum.
Datum may be mean sea level or any assumed local level.
* Stage can be measured by :
- Mannual gauge: (a) Staff Gauge and (b) Wire Gauge
- Automatic Gauge : (a) Float gauge recorder and (b) Bubble gauge recorder.
1. Mannual method :
1(a). Staff Gauge: A staff gauge is made of wooden material of low coefficient of thermal conductivity with respect to temperature and moisture. It is placed along the cross section of a river. It is fixed rigidly to a structure such as abutment, Pier or wall, etc.1(b). Wire Gauge: In this method a weight is lowered with the help of wires from above a structure such as Bridge or any similar structure to touch the water surface. The length of water wire used will give rise or fall of water surface elevation.
2. Automatic method:
2(a). Float gauge recorder: In this method a float is balanced by means of a counter weight with the help of pulley. A stilling basin is used to protect the float from the debris or high wave action of water.
The rise or fall of float will give water surface elevation through an arrangement made in the float gauge.
2(b). Bubble gauge recorder : In this method a compressed air or gas is made to flow at a small rate to touch the water surface. The pressure applied to the gas bubble is measured by the pressure gauge. The applied pressure will be equal to the water pressure.
#Measurement of Velocity :
- By Float
- By Current meter
In this method, a float is kept on the water surface. Let us consider a float will travel a distance 'L' metre in a time interval of t seconds.
The surface velocity of river is given by
V = L/t
2. Current meter:
It consists of rotating elements which rotates due to reaction of stream currents. The number of revolutions per second are measured through an arrangement in the current meter.
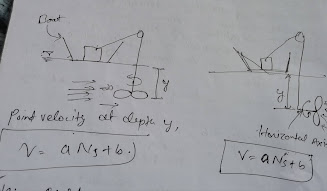
It is used to measure point velocity at any depth.
The characteristic equation of point velocity at any depth is given by
V = a*Ns + b
Ns= number of revolution per sec.
a and b= current meter constant.
There are two types of current meter:
- Vertical axis current meter
- Horizontal axis current meter
- Mean velocity in turbulent is 85% to 95% of surface velocity.
- For shallow stream mean velocity is taken as point velocity at 0.6y depth from surface. V = V at 0.6y. This is also called one point method or wadding technique.
- For deep stream, mean velocity is taken as average of point velocity at 0.2y depth & 0.8y depth from free surface along same line of action. This is also called two point method.
- Area velocity method
- Moving boat method
- Dilution method
- Ultrasonic wave method
- Electromagnetic method
- Slope area method
- Hydraulic structures such as notches, weir, barrage, spillway, etc.
- Site should be stable.
- It should be easily accessible throughout the year.
- There should not be back water effect in the channel.
- Stream should have well defined cross sectional area which does not change in various season.
- If stage discharge relationship of a river does not vary with respect to time then such a control is called permanent control, whereas if stage discharge relationship will vary with respect to time then such a control is called shifting control.
- For unsteady flow in a flood, a stage discharge relationship is expressed by a curve which is called loop rating curve.





Good information,I like reading your posts.
ReplyDelete